What Is ADSL Internet Technology ?
In the last post, we have seen a brief overview of the DSL (digital subscriber line) technology, that we use in our daily life. Now in this post, we will further dig deep inside the first variety of DSL i.e. the ADSL (asymmetric DSL ) internet technology. So let’s start the discussion.
What is ADSL Internet in reality (ADSL Meaning) ?
The long-form of ADSL is Asymmetrical DSL . It provides a higher bit rate in the downstream direction (from the Internet to the user) as compared to the bit rate in the upstream direction (from user to Internet). This is why it is called as asymmetrical.
ADSL divides the bandwidth utilizing a twisted pair cable of 1 MHz into 3 bands.
1. The starting band is between 0 and 25 kHz. It is used in a simple telephone (Plain Old Telephone Sets – POTS). This service uses only 4 kHz of this band the rest is implemented as the guard band in order to separate the voice channel from the data channels.
2. The second band is from 50 kHz to 200 kHz. It is used for upstream data communication.
3. The third band is from 250 kHz to I MHz. It is used for downstream data communication.
ADSL technology is designed for home users. It is not suitable for business applications because such applications need larger bandwidth than home users.
Use of existing Local Loop in ADSL
The ADSL uses the existing local loop and still it can support very high data rates. Actually the twisted pair local telephone cable can support the bandwidth upto 1.1 MHz. The bandwidth reduces to 4 kHz due to the filters installed at the end of line.
Hence the existing local loop with this modification can have a bandwidth of 1.1 MHz and ADSL can make use of the existing loop for voice as well as data communication.
The existing local loops can handle bandwidths up to 1.1 MHz.
Adaptive Technology in ADSL
The bandwidth of 1.1 MHz is not always available practically. It will depend on various factors such as distance, cable size, type of signaling etc. So ADSL has been designed, to operate as an adaptive technology. That means depending on the conditions and actually available bandwidth, the data rate of ADSL is adjusted.
ADSL is adaptive technology. The system uses a data rate based on the condition of the local loop line .
Modulation Techniques in ADSL
Two modulation techniques can be used for ADSL :
- Carriers amplitude/phase (CAP)
- Discrete multitone (DMT)
CAP is a modulation technique that is similar to QAM but with one important difference i.e. the carrier signal is eliminated.
Discrete Multltone Technique (DMT) in ADSL : DMT is the standard modulation technique for ADSL. It is a combination of QAM and FDM techniques .
Typically the available bandwidth of 1.1 MHz is divided into 256 channels. However, this is not a rule. The division may change system to system.
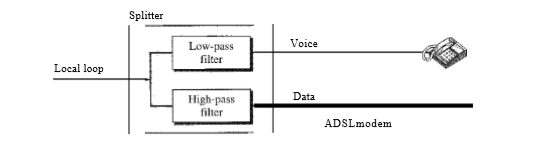
Channel ‘0’ is reserved for voice communication. Channels 1 to 5 are called the Idle channels as they are not at all used. These channels create a guard band between the voice and data channels. Channels 6 to 30 (25 channels) are used for the upstream data transfer and control. 24 channels are for data transfer and one channel for control.
The channels 31 to 255 (225 channels) are allotted for downstream data transfer and control. Out of 225 channels. one is reserved for control and the remaining 224 are reserved for data.
ADSL Modem !!
The ADSL modem installed at the user’s site is shown in fig :
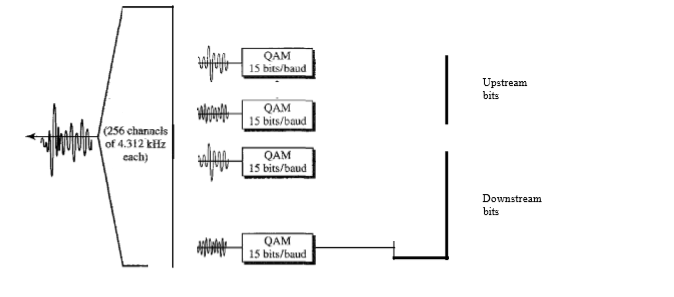
The local loop (pre-existing telephone wire) is connected to the filter which separates voice and data from each other. The voice goes to the telephone instrument. The data goes to the ADSL modem which modulates it using DMT to create the upstream and downstream channels.
Note that the splitter needs to be installed at the customer’s premises, normally by a technician from the telephone company. The voice line can use the existing telephone wiring in the house, but the data line needs to be installed by a professional. All this makes the ADSL line expensive.
ADSL Lite !!
The setup of splitters on the edge of their assumptions and also the wiring for the information line could be costly and impractical enough to discourage many readers. A modified new variant of ADSL technology named ADSL Lite (or Universal ADSL or splitters ADSL) can be obtained for all these subcribed users.
This technology permits an ADSL Lite modem to be plugged into a phone jack and attached to your pc. The splitting is completed in the phone company.
It can offer a maximum downstream data speed of 1.5 Mbps and an upstream data rate of 512 kbps. Finally, we reach the end of this post. Stay tuned for more interesting stuff.
Aric is a tech enthusiast , who love to write about the tech related products and ‘How To’ blogs . IT Engineer by profession , right now working in the Automation field in a Software product company . The other hobbies includes singing , trekking and writing blogs .




