What is MPLS in Networking ? (Multiprotocol Label Switching)
In the last post, we have seen the comparison between wifi and wimax feature. Now in this post we will further explore the next important telecommunication network called the Multiprotocol Label Switching technique.
When IETF was developing the integrated services, several router vendors were developing a new and better forwarding method called as label switching or tag switching. IETF eventually standardized this idea under the name MPLS (MultiProtocol Label Switching).
What is MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching) ?
Multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) is a mechanism in high-performance telecommunication networks that directs data from one network node to next based on short path labels rather than long network addresses, avoiding complex lookup routing tables.
The labels basically identify the virtual paths (links) between distant nodes rather than the end points. MPLS further works with various network protocols (i.e multiprotocol) like IPv4 network, IPv6 network, ATM network, Frame relay networks etc. It supports a range of access technologies including DSL etc .
In this method, a label is added in front of each packet and the rooting is done on the basis of this label and not on the basis of the destination address.
MPLS is a protocol-independent transport mechanism. In an MPLS network, data packets are assigned specific labels. In this, the packet forwarding decisions are made only depending on the contents of this label without the need to examine the packet.
This allows one to create end to end circuits across any type of transport medium using any protocol.
MPLS operates at a layer that is in between layer 2 and layer 3 and thus it is referred to as layer 2.5 protocol. It has been designed to provide a unified data-carrying service for both circuit-based clients and packet-switching clients network.
IP routers use destination-based forwarding to determine the next hop of a packet . This was traditionally implemented in software and viewed as too slow for core networks.
A router that supports MPLS is called label switching router (LSR) or transit router, unlike an IP router, an LSR separated the control and forwarding components as shown in figure. The control components run traditional IP routing protocols and new MPLS signaling protocols.
The forwarding components which can be implemented by any layer 2 technology performs label switching and provides fast data paths.
A LSR that interfaces to a traditional IP router are called an edge LSR . It may be ingress (entering) LSR or egress (exiting) LSR. The ingress LSR receives traffic from a non MPLS router while the egress LSR sends traffic to non MPLS router.
In MPLS a unidirectional connection through multiple LSR’s is called a label switching path (LSP) . A group of packets that are forwarded in the same manner (along the same path) in an MPLS domain are said to belong to same forwarding equivalence class (FEC) .
The assignment of a particular packet to a specific FEC is done only at an ingress LSR where the label for the packet is also created. From there on other LSR’s use, the label to determine the next-hop and the label is removed at an egress LSR.
MPLS (multiprotocol label switching) Header Format
The first step in MPLS will be to decide the place of the label in the IP packet. In the IP packet, there is no place available for the label because it was not designed for virtual circuits. Therefore a new MPLS header is added in front of the IP header as shown :
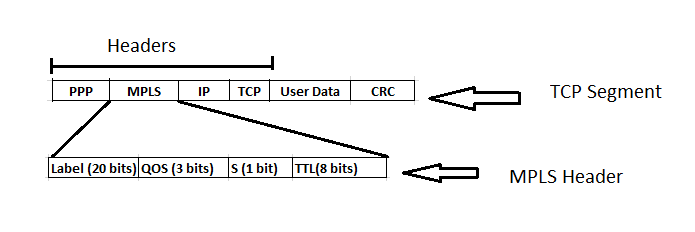
Label : It is 20-bit label and its value is equivalent to a virtual circuit identifier. The Label fielo is a 20 bit field that holds the index .
Experimental Field (QOS) : A 3 bit traffic class field for QOS , priority and ECN . The 3-bit QoS (Quality of service) field indicates the class of service.
S : A ‘1 bit’ field present at the bottom of the stack flag . If this is set (S = 1) , it signifies that the current label is the last in the stack. The 1-bit S field relates to the stacking of multiple labels in the hierarchical networks.
TTL : It is 8 bit time to live field.
When a label is attached to a packet at an ingress LSR , the LSR is said to perform a label push (include a label header) . Subsequent LSR’s in the MPLS domain only SWAP the incoming label to the outgoing label. When the packet leaves MPLS domain , the egress LSR performs a label pop (removes the label header) by removing a label.
Working Of MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching)
When an MPLS packet or cell arrives at an MPLS router, the label is used as an index into the lookup table to find out the correct outgoing line and also the new label to be used. This new label contains the address of the next MPLS router. The labels have to be remapped at every hop, similar to that in the virtual circuits.
The routers normally group multiple flows that end at a particular router or LAN and use a single label for them. The flows grouped under a single label belong to the same FEC (Forwarding Equivalence Class).
Labels are distributed between edge LSRs and LSRs using the label distribution protocol(LDP) . LSRs is an MPLS network regularly exchanging labels and reachability information with each other using standardized procedures in order to build a complete picture of the network they can then use to forward packets.
There are two procedures for managing MPLS paths i.e. Label distribution protocol (LDP) and the Resource reservation protocol for traffic engineering (RSVP- TE) .
MPLS is mainly used in TCP/IP network , Virtual private LAN service (VPLS) , Virtual private network, and in ATM network.
GMPLS is the generalized MPLS that allows a node with multiple switching technologies like packet switching , TDM switching , SONET/SDH switching, optical switching etc.
In the next post, we will understand the ATM protocol in detail. So stay tuned.
Aric is a tech enthusiast , who love to write about the tech related products and ‘How To’ blogs . IT Engineer by profession , right now working in the Automation field in a Software product company . The other hobbies includes singing , trekking and writing blogs .




