Wide Area network(wan),Local Area Network(lan), Metropolitan Area Network(man), Personal Area Network(pan) and Campus Area Network(can)
Spoiler – This post is long yet interesting!!
For a quick summary of the topics discussed in this post, you may directly scroll down to view the differences in features of LAN, WAN and MAN.And for those who want a detailed overview of this topic(i.e Wide area network(wan),Local Area Network(lan), Metropolitan Area Network(man), Personal Area Network(pan), Campus Area Network(can)), please be patient and continue.
In my previous post we have seen various communication types by virtue of which successful communication can be established. Now, there are many other factors that have to be taken care of while designing any data network. The two most important factors to be determined are:
- Types of transmission technology and ,
- Scale (physical size of the network)
1. Transmission technology
There are mainly two types of technologies that can be implemented i.e Broadcast network and point to point networks.
In Broadcast networks, all nodes(devices) in the network share the same channel, and the message(in the form of packets of data) sent by any device in the network, is received by all the others.
Further, a special code in the address field is used for addressing any particular(desired) device in the channel. Thus, when a packet is received, a machine checks for the address field.
In point to point network as the name suggests, there exist many connections between any pair of machines. Most of the point-to-point connections mainly use an actual length of any wire or a cable in order to connect the two far ends.
The packets sent by any device have to follow multiple routes of different lengths before reaching the desired device.Thus properly designed routing algorithm plays a vital role here.
2. Network Scale
Based on the physical size, we can classify the network hardware configuration. The category into which a network falls is normally determined by their respective size.
A LAN generally covers an area which will be less than 2 miles , a WAN can further be worldwide. Networks of any size in between are normally referred to as the metropolitan area networks (MAN) and can span over tens of miles.
For clarity, you may refer below table:
| Multidevices Distance | Devices are located in | Example of network |
| 1 m | Same System | Multicomputer |
| 100 m | Same building | LAN |
| 1 km | Same Campus | LAN |
| 100 km | Same state | WAN |
| 1000 km | Same Continent | WAN |
| 10000 km | Same Planet | Internet |
Network is mainly divided into the following three categories(more detail in the next section ):
- Local Area Network
- Metropolitan Area Network
- Wide Area Network
Network Classification by their Geography:
Computer networks can be classified based on the geographical area they cover i.e. the area over which network is spread.
Such classification can be given as:
- PAN(Personal Area Network)
- LAN(Local Area Network)
- MAN(Metropolitan Area Network)
- WAN(Wide Area Network)
- CAN(Campus Area Network)
In this section ,we will discuss the following categories of networks.i.e Wide area network(wan),Local Area Network(lan), Metropolitan Area Network(man), Personal Area Network(pan), Campus Area Network(can)
What is Local Area Networks (LAN) ?
The Local Area Network(LAN) is a network that is designed in order to operate over a small physical area such as in a factory , buildings or a group of corporate offices. A local area network is basically privately owned and further links the devices in any campus , single office, or buildings. Currently, LAN size is basically limited to a few kilometers. LANs are trusted widely in a variety of applications.
Early LANs had data rates ranging in between 4 to 16 megabits per second (Mbps) range.However, at present, the speeds generally range between 100 or 1000 Mbps.
LANs are generally very convenient to troubleshoot and build. The personal computers (PC) and the workstations in the office are well connected to each other via LAN.
The exchange of data messages and the sharing of allocated resources between various devices becomes easy due to the use of LAN.
LAN mainly uses a layered architectural framework and they are further capable of operating at a very high data rate (hundreds of Mbits/sec) .
Depending upon the requirements of any organization and the kind of technologies implemented i.e. a LAN can be very simple as a very few computers and a printer at home or it can contain many computers in a company and include voice ,sound and video peripherals.Wireless LANs are the newest evolution in the LAN technology
LANs are widely used in order to allow the resources to be shared among the PCs or workstations. The resources that are to be shared can be hardware like a printer or any softwares or data.
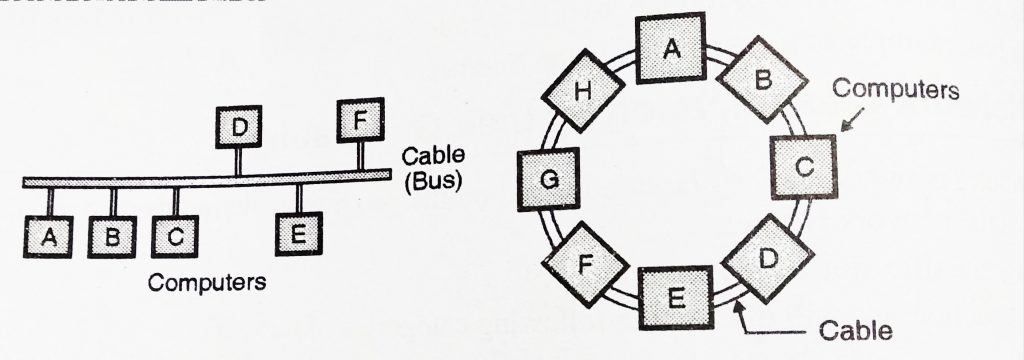
LANs are also distinguished from MAN’s and WAN’s based on the transmission media that they use and topology. In general, any given LAN will use only one type of a transmission medium. The most common networking topologies used are bus,ring and star.
LANs are mainly designed to allow the resources that are to be shared among the personal computers (PCs) or any workstations. for eg, one of the computers may be given a larger capacity disk drive and then it may become a server to the clients.
The software can then be saved (stored) on this central server and also can be used as required by the complete group. This scenario is common in many workstations.
State and Dynamic broadcast networks:
- Any broadcast network can further be classified into two types namely:
- Static networks and
- Dynamic networks.
The classification is basically based on how the common channel has been allocated.
In the static allocation, each of the machines is allowed to broadcast only in its assigned allotted time slot.
The static allocation mainly wastes the assigned channel capacity when any machine doesn’t want to transmit in its allotted time slot.
Hence in most of the systems generally try to allocate the channel dynamically i.e.on demand.
LAN components:
A number of the essential LAN components are the following:
- Workstations
- File servers.
- Gateway
- Network interfacing unit.
- Active and passive hub.
- Lan cables or communication channels
Workstation:
Workstation relates to any single computer (PC) or any specific individual. An interaction ability is further added in order to enable it for networking.
File server:
The file server is a computer application that generally allows the sharing of software,hardware and data resources by running unique special softwares.
Gateway : It facilitates the movement of data from anyone LAN to the other LAN efficiently.
Network Interfacing Unit(NIU)
This is a device which is comprised of an equipment (hardware) along with software . It uses microprocessor to regulate interaction and access in a communication network.
LAN cables or communication channel:
A cable is employed (used) for connecting any computer in a LAN.The communication from one computer to others takes place over the cables.So cables are called communication channels. The twisted pairs ,coaxial cables or optical fiber cable are used in LANs.
What is Metropolitan Area Network(MAN) ?
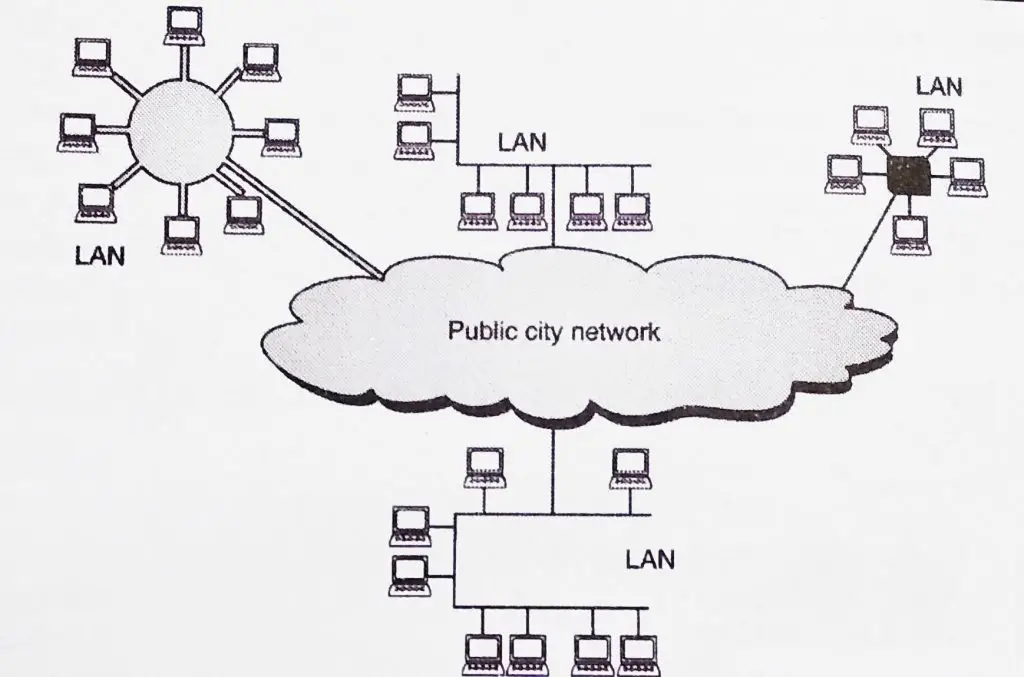
A MAN is simply a bigger (modified) version of a LAN that precisely uses similar technology. It is developed in order to extend over a very larger area such as an entire city.
It generally covers the area inside any city or a town. It is designed mainly for customers who need very high-speed connectivity to the Internet, and also have the endpoints being spread over any city (or part of city) .
The MAN could be by means of a single network as being a cable network system or it can be rather a mixture of numerous LANs as shown in fig.
A MAN could be wholly owned and operated along with a private company or it is also a service supplied by a general public company, like a telephone company that is regional .
A MAN is based on the framework of the IEEE 802.6 standard or it can also be known as the Distributed Queue Dual Bus(DQDB).
Each bus has a device that initiates the transmission activity called as the head end.
Traffic that is destined for a computer to the right of the sender uses the upper bus and to the left uses the lower bus.
An example is the cable TV network that originally designed for cable TV, but today can also be used for the high-speed data connection to the Internet.
Also MAN is the part of a telephone company network that can provide a very high-speed DSL line provided to the respective customer.
What is Wide Area Network (WAN) ?
When any network spans over a large area or when the computers that are to be connected to one another are at widely separated distances, then a local area network can’t be used.
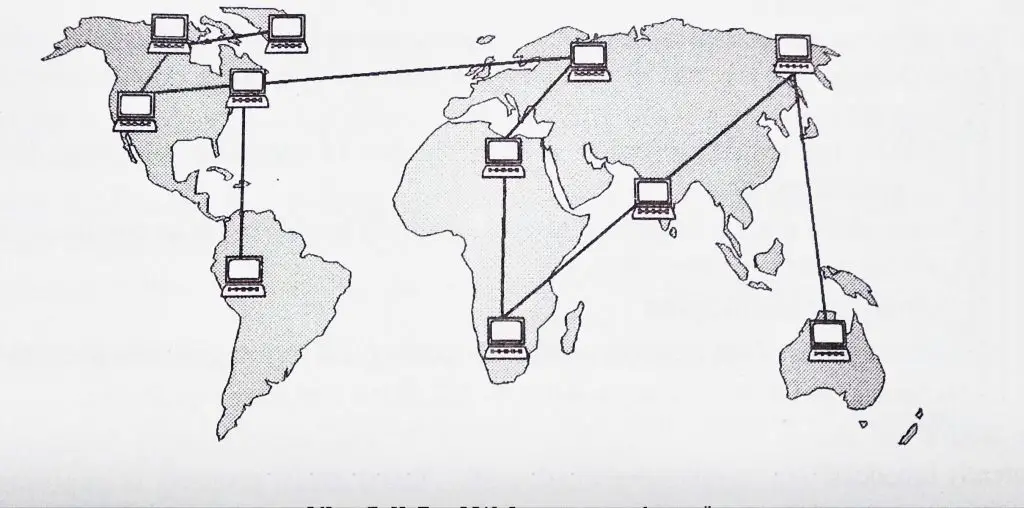
A WAN basically provides a long-distance transmission of image, data , video, and audio information over very large geographic areas that may comprise of a continent, country, or even in the complete world.
For such a situation a Wide Area Network(WAN) must be installed .The communication will be in between different users of “WAN” is established using a number of leased telephone lines or satellite links and in similar channels.
It is cheaper and much more efficient to use any phone network for the links.A WAN network can be very much complex as the backbones that will connect the internet or as simple as the dial-up line that will connect the basic household computer to the Internet.
Mostly the wide area networks basically used for transferring very large blocks of data among its respective users . Since the data will be from the existing records , the time taken for the data to transfer isn’t one of the important parameters.
An example of WAN is clearly visible in an airline reservation system.The terminals are generally located all over the country, using this the reservations can be done.
It is indeed very important here to note that all the terminals mainly uses the same centralized common data that is provided by the central reservation computers.
Due to the larger distances present in the WAN network, the propagation delays and the variable signal travel times are some of the major problems.
Thus most of the WANs are not used for the time-critical applications. As already explained earlier that the WAN network is more suitable for the transfer of data from one user to the other user which is not a time critical application. WANs are mainly the packet switching networks.
The switched WAN will connect the end systems, which usually comprise of a router (internetworking connecting devices) that will further connect to the other LAN or WAN networks.
The point-to-point WAN is basically a line that is leased from any telephone or cable TV provider that further connects to a household computer (PC) or any small LAN to an Internet service provider (lSP).
A WAN basically provides very long-distance transmission of message data , voice image and also any video information over a large geographical area that may mainly comprised of a continent ,a country or even the coomplete world as shown in below fig.
An example of a switched WAN is an asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) network (as explained in later posts), which is a specific network along with a fixed data sized unit packets called as the cells.
HOST: Host is a large computer.It can provide services to many computers.The services provided are:
- Providing computing capabilities
- Providing access to the database.
WAN contains a large collection of machines for running application programs. All the devices connected called as hosts and all are connected by Subnet. The main function of the subnet is to carry message packets from the host to host. It contains mainly two parts i.e Transmission lines and Switching network.
Transmission lines help in transferring data packets from one device to other,and the switching elements are used to connect multiple machines(hosts). When any data arrives on an incoming line, then the switching element has to then choose an outgoing line on which it has to be forwarded.
These packet switching nodes(switching elements) transfer data via one or more intermediate routers. The packet will then be received by an intermediate node. The data packet will then be stored in a router(node) until the required output line will be free and then forwarded.
If two routers (which are not connected) want to take part in data exchange, then it will be done indirectly via other routers .
What is PAN (Personal Area Network) ?
This network is the simplest of all the networks . This provides data exchange between individual’s workspace i.e in between personal computers, smartphones, and other digital sharing devices. This can be done via wired media or wireless(Bluetooth, infrared, Zigbee etc).
However for wireless transmission of data packets,this supports a very small range ranging from few centimeters to few meters(a piconet typically has a range of 10 meters i.e 33 ft).
What is CAN (Campus Area network) ?
A campus network as the name represents , is simply a local area system (LAN serving an organization, government agency, university, or comparable organization).
The users in a campus area network are dispersed more commonly (in a sense that is geographical) than in a single LAN, but they are usually not as spread as they might be in a wide area network (WAN)
A campus area system (CAN) is simply a network of multiple interconnected local area sites (LAN) in a very restricted area that is geographical. A CAN is smaller than the region that is with WAN or even a metropolitan area system (MAN).
A CAN is further known as the corporate area network (CAN). It is much cost-effective and multidepartmental accessible , further it will be single shared data rate.
Listed below are examples of the CAN implementations:
- Stanford University’s SUNet network and
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology’s (MIT) Project Athena
Apart from all the above-mentioned classification, we may also have some other setups of connected devices in this geographical arena.Two most important of those are :
- Wireless Networks
- Internetworks
In Wireless Networks , we mainly deal with the devices having the capability of making data exchanges through any wireless media.We can take example of mobile computers such as notebook computers etc. Wireless LAN is another example of a wireless network.
It is also possible to have wired and wireless networking combo.This type of network can be established while going to office, or in car,bus, aeroplanes etc for reading emails and for other purpous. The most important use of this network has been implemented in Military operations.
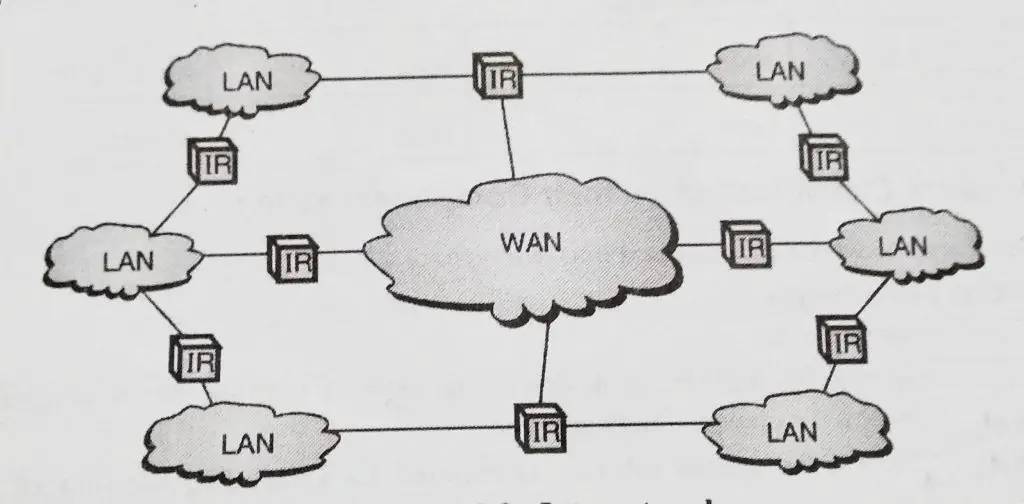
Internetwork connections mainly consist of a combination of two or more networks such as LAN and WAN network.
For a quick summary, you may refer to below table for ready reference:
| Parameter | LAN | WAN | MAN |
| Bandwidth | Low | High | Moderate |
| Propagation Delay | Short | Long | Moderate |
| Data Rate | High | low | Moderate |
| Channel medium | Coaxial cable | PSTN or satellite links | optical fiber cables,coaxial cables,wireless |
| Geographical Area Covered |
Small | Very large(states or countries) | Moderate(city) |
| Ownership of network | Private | Private or public | Private or public |
So, here comes the end of this wonderful post.Stay tuned for the next interesting topic i.e Peer to peer and Client-Server network features and model specifications.
Aric is a tech enthusiast , who love to write about the tech related products and ‘How To’ blogs . IT Engineer by profession , right now working in the Automation field in a Software product company . The other hobbies includes singing , trekking and writing blogs .




